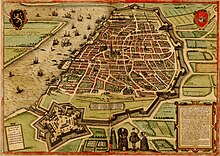
Cultural Timeline of Antwerp
A brief overview of the historical and artistic events that shaped the city of Antwerp
Gallo-Roman Settlement to 15th Century
|
Year |
Event |
|
150-250 CE |
A Gallo-Roman settlement existed in the center of Antwerp at Willem Ogierplaats |
|
700 CE |
The name Andoverpis appeared in a written source called the Vita Eligii |
|
978 CE |
The Treaty of Margut-sur-Chiers recognized the river Scheldt as the border between Neustria and Lotharingia |
|
980 CE |
German Emperor Otto II granted Antwerp a margraviate and built a fortification on the wharf |
|
1213 |
France occupies Flanders |
|
1250 |
Construction of the second Vleeshuis, city butchery and Guildhouse of the butchers |
|
|
|
|
1406 |
Antwerp became part of the Duchy of Brabant |
|
1442 |
Guild of Saint Luke granted privileges. The guild was a professional association of painters, sculptors, engravers, and other artists in Antwerp. |
|
1477 |
Quaeye Werelt revolt; Joyous Entry of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor into the city; Violieren chamber of rhetoric founded: a literary society that promoted the Flemish language and culture. |
|
1481 |
Establishment of a printing press by Matt. Van der Goes. Antwerp became one of the leading centers of printing and publishing in Europe. |
|
1491 |
One of the world’s “first” illustrated advertisements printed in Antwerp. The advertisement was for a book by Werner Rolevinck called Fasciculus temporum. |
16th Century
|
Year |
Event |
Description |
|
1503 |
Construction of the third Vleeshuis |
The current building that served as the city butchery and guildhouse of the butchers |
|
1515 |
Joyous Entry of Charles V |
Holy Roman Emperor, into the city |
|
1518 |
Notre Dame Cathedral completed |
The cathedral is a masterpiece of Gothic architecture and houses many artworks, including paintings by Rubens |
|
1520 |
Het Steen fortress rebuilt |
Het Steen is the oldest building in Antwerp and was originally part of the city's fortifications |
|
1523 |
Church of St. Andrew built |
The church is a fine example of Brabant Gothic style and contains many artworks and relics |
|
1528 |
Merten de Keyser started his business |
He printed many important works, including the first complete Bible in Dutch |
|
1531 |
The Bourse of Antwerp opened |
The first purpose-built exchange, was a place where merchants and bankers could trade and exchange currencies, commodities, and bills of exchange. It was a precursor of modern stock exchanges |
|
1552 |
The Girls' orphanage built |
The orphanage was founded by the Sisters of Charity and provided shelter and education for orphaned girls |
|
1555 |
Christophe Plantin established his business |
He printed many influential works, including the Polyglot Bible, a multilingual edition of the Bible. His printing house, the Plantin-Moretus Museum, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site |
|
1555 |
Holy Roman Emperor Charles V abdicated |
He divided his territories between his son Philip II of Spain and his brother Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor. Philip II inherited the Spanish Netherlands, which included the Low Countries (present-day Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg). |
|
1560s |
Antwerp Citadel built |
The citadel was a fortress that controlled the access to the city and the river. It was used by various rulers to suppress rebellions and sieges |
|
1565 |
City Hall built |
The city hall is a splendid example of Renaissance architecture and a symbol of civic pride and autonomy |
|
1566 |
Protestant Reformation riots |
The riots were part of the Iconoclastic Fury, a wave of iconoclasm that swept across the Low Countries. Protestants destroyed many Catholic images and statues in churches and monasteries |
|
1567 |
Battle of Oosterweel |
Occurred near the city on 13 March. The battle was the first major confrontation of the Eighty Years' War, a revolt of the Dutch provinces against the Spanish rule. The rebels were defeated by the Spanish troops |
|
1570 |
Theatrum Orbis Terrarum atlas published |
The atlas was the first modern atlas of the world, compiled by Abraham Ortelius, a cartographer and geographer from Antwerp. (Zeeland en Brabant by Ortelius) |
|
1571 |
Church of St. Paul built |
The church is a former Dominican monastery that contains many artworks, including paintings by Rubens and Van Dyck |
|
1572 |
Antwerp Citadel completed |
|
|
1576 |
Sack of Antwerp |
On 4 November, John III van de Werve, Lord of Hovorst, was killed by the Spanish forces. The sack was a brutal attack by the Spanish mutineers on the city, resulting in thousands of deaths and massive destruction |
|
1577 |
Antwerp Citadel partially dismantled |
|
|
1579 |
City joined the Union of Utrecht |
The union was a confederation of the northern Dutch provinces that opposed the Spanish rule and formed the basis of the Dutch Republic |
|
1582 |
Prince William I of Orange injured |
The leader of the Dutch revolt was injured in an attack at Antwerp. He survived the assassination attempt by a Catholic fanatic, but was killed two years later in Delft |
|
1585 |
Siege of Antwerp ended (Michael Pye) |
Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma, in power. The siege was a prolonged military blockade by the Spanish army that lasted for 14 months. The city surrendered and the Spanish troops occupied the city. The siege marked the end of Antwerp's golden age and the beginning of its decline |
17th Century
|
Year |
Event |
Description |
|
1603 |
Rockox House built |
Nicolaas II Rockox built the Rockox House, now a museum displaying his art collection |
|
1609 |
Twelve Years' Truce signed |
Temporary cessation of hostilities between the Spanish and the Dutch, allowing economic recovery and cultural development in Antwerp |
|
1615 |
Church of Augustinians built |
Center for religious art and architecture, hosting famous artists such as Rubens, Van Dyck, and Jordaens |
|
1621 |
Carolus Borromeuskerk built |
Baroque masterpiece designed by the Jesuits and decorated by Rubens |
|
1635 |
Joyous Entry of Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand |
Ferdinand, governor of the Spanish Netherlands, entered the city with great pomp and ceremony. Map of East Flanders by Merkator |
|
1638 |
Battle of Kallo |
Naval engagement between the Dutch and the Spanish fleets, resulting in a Dutch victory |
|
1644 |
House of the Tailors rebuilt |
Guildhall of the tailors, one of the most influential and wealthy guilds in Antwerp |
|
1646 |
Hall of the Carpenters rebuilt |
Guildhall of the carpenters, responsible for the construction and maintenance of the city's buildings and fortifications |
|
1646 |
Siege of Antwerp failed |
Attempt by Frederick Henry, stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, to capture Antwerp from the Spanish, but was repelled by the city's defenders |
|
1648 |
River Scheldt closed to navigation |
Per Treaty of Münster, ending the Eighty Years' War and recognizing the independence of the Dutch Republic, but hampering Antwerp's trade and prosperity |
|
1648 |
Joyous Entry of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria |
Leopold Wilhelm, governor of the Spanish Netherlands, entered the city with great splendor |
|
1656 |
St. James' Church built |
Gothic edifice containing the tomb of Rubens and many other artworks |
|
1663 |
Royal Academy of Fine Arts founded |
One of the oldest and most prestigious art schools in Europe, producing renowned artists such as David Teniers the Younger, Jacob Jordaens, and (in the 20th century) James Ensor |
18th Century
|
Year |
Event |
Description |
|
1713 |
Cession to Austria |
As a result of the War of the Spanish Succession, the Spanish Netherlands, including Antwerp, were ceded to the Austrian Habsburgs. This marked the beginning of the Austrian Netherlands period, which lasted until the French Revolution in 1794. |
|
1745 |
Royal Residence built on the Meir |
The residence was a palace that was used by the Austrian governors of the Southern Netherlands, such as Maria Theresa and Charles VI. |
|
1746 |
Osterrieth House built on the Meir |
The house was a mansion that belonged to the Osterrieth family, a wealthy banking dynasty. The house is a fine example of Rococo architecture and decoration. |
|
1750 |
Royal Horticultural and Agricultural Society exhibitions began |
The society was a scientific and cultural organization that promoted the study and improvement of horticulture and agriculture in Antwerp and Belgium. |
|
1755 |
Royal Palace built |
The palace was a residence that was used by the French governors of the Southern Netherlands, such as Louis XV and Napoleon. |
|
1790 |
Population: 40,000 |
|
|
1795 |
City became capital of French département Deux-Nèthes |
The city was annexed by France during the French Revolutionary Wars and became part of the French Republic. |
19th Century
|
Year |
Event |
Description |
|
1802 |
Quays built on Schelde River |
The quays were a series of embankments and docks that improved the navigation and trade on the river. |
|
1805 |
City Library opened in City Hall |
The library was a public institution that offered access to books and information to the citizens of Antwerp. |
|
1810 |
Royal Museum of Fine Arts founded |
The museum is a major art museum that houses a collection of paintings, sculptures, and drawings from the 14th to the 20th century, including works by Rubens, Van Dyck, and Ensor. |
|
1811 |
Bonaparte Dock built |
The dock was a large basin that was constructed by Napoleon to accommodate his naval fleet. |
|
1813 |
Willem Dock built |
The dock was a smaller basin that was constructed by Napoleon to accommodate his naval fleet. |
|
1815 |
City became part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands |
The city was liberated from the French occupation and became part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, a new state that was created after the Congress of Vienna. |
|
1816 |
Jewish Community established |
The community was formed by the Ashkenazi Jews who settled in Antwerp after the emancipation granted by the Dutch king. |
|
1818 |
Fortresses built |
The fortresses were a series of defensive structures that were built around the city to protect it from foreign invasions. |
|
1823 |
Dutch King Willem I opened a shipyard at Rotterdam-Antwerp |
The shipyard was a naval and commercial facility that was built by the king to boost the economy and trade of Antwerp. |
|
1830 |
Belgian rebels occupied Antwerp during the Belgian Revolution |
The revolution was a nationalist uprising that aimed to secede from the Kingdom of the Netherlands and establish an independent Belgian state. |
|
1831 |
Jan van Speyk blew up his gunboat in Antwerp to avoid capture by the Belgians |
Van Speyk was a Dutch naval officer who became a national hero for his act of self-sacrifice and loyalty to the Dutch king. |
|
1832 |
November–December: City besieged by French forces |
The siege was a military operation that was conducted by the French army to support the Belgian rebels and force the Dutch troops to surrender the city. |
|
1834 |
Medical Society founded |
The society was a professional association of doctors and surgeons that aimed to improve the medical education and practice in Antwerp. |
|
1843 |
Zoological Garden founded |
The garden is one of the oldest and largest zoos in the world, and hosts a variety of animals and plants. |
|
1846 |
Population: 88,487 |
|
|
1848 |
Jan Frans Loos became mayor |
Loos was a liberal politician and lawyer who became the first elected mayor of Antwerp. He initiated many reforms and improvements in the city, such as the expansion of the port, the construction of the railway, and the establishment of public education. |
|
1852 |
Wuyts art gallery opened |
The gallery was a private museum that displayed the art collection of Florent van Ertborn, a former mayor of Antwerp and a patron of the arts. |
|
1853 |
Institut Saint-Ignace inaugurated |
The institute was a Jesuit school that offered secondary and higher education in Antwerp. |
|
1859 |
Berchem and Borgerhout became part of city |
The two municipalities were annexed by Antwerp to accommodate its growing population and territory. |
|
1860 |
Kattendijk built |
The Kattendijk was a canal that connected the Scheldt river with the Bonaparte and Willem docks. |
|
1864 |
Museum of Antiquities opened |
The museum was a public institution that exhibited a collection of ancient artifacts and coins from various civilizations. |
|
1866 |
Cholera epidemic |
The epidemic was a public health crisis that caused many deaths and suffering in Antwerp. |
|
1867 |
School of Music founded |
The school was a conservatory that provided musical education and training in Antwerp. |
|
1870 |
Fort Merxem constructed |
The fort was a part of the National Redoubt, a defensive system that was built around Antwerp to protect it from a possible German invasion. |
|
1871 |
International Geographical Congress held |
The congress was a scientific meeting that gathered geographers and explorers from different countries to discuss and exchange ideas on geography. |
|
1872 |
Exchange building and Flemish Theatre built |
The exchange building was a neoclassical edifice that housed the stock exchange and the chamber of commerce. The Flemish Theatre was a cultural venue that promoted the Flemish language and drama. |
|
1873 |
Horsecar trams began operating |
The trams were a form of public transportation that used horse-drawn carriages on rails. |
|
1874 |
Demolition of Antwerp Citadel began |
The citadel was demolished to make way for the expansion of the city and the port. |
|
1876 |
Royal Geographical Society of Antwerp founded |
The society was a scientific and cultural organization that promoted the study and exploration of geography and related disciplines. |
|
1877 |
Plantin-Moretus Museum opened |
The museum was a former printing house that belonged to the Plantin and Moretus families, who were famous printers and publishers in Antwerp. The museum preserves the original equipment, books, and artworks of the printing house. |
|
1879 |
Population: 173,600 |
|
|
1880 |
Royal Antwerp Football Club formed |
The club is one of the oldest and most successful football clubs in Belgium. |
|
1881 |
Antwerp Water Works constructed |
The water works was a facility that supplied clean and safe drinking water to the city. |
|
1883 |
Library building opened |
The building was a neoclassical structure that housed the city library and the museum of fine arts. |
|
1884 |
Museum Mayer van den Bergh built |
The museum was a private institution that displayed the art collection of Fritz Mayer van den Bergh, a wealthy art collector and connoisseur. |
|
1885 |
Exposition Universelle d'Anvers (world's fair) held |
The fair was a large-scale exhibition that showcased the achievements and innovations of various countries and industries. |
|
1885 |
Temperance conference held |
The conference was a social movement that advocated the moderation or abstention of alcohol consumption. |
|
1891 |
Gazet van Antwerpen newspaper began publication |
The newspaper is one of the oldest and most popular newspapers in Antwerp and Belgium. |
|
1892 |
Société Anversoise du Commerce au Congo in business |
The company was a trading and shipping enterprise that operated in the Congo Free State, a large African territory that was owned by King Leopold II of Belgium. |
|
1893 |
Koninklijke Vlaamse Opera (Flemish Opera) founded |
The opera is a cultural institution that performs operas and musicals in the Flemish language. |
|
1894 |
Exposition Internationale d'Anvers (world's fair) and Universal Peace Congress held |
The fair was another large-scale exhibition that showcased the achievements and innovations of various countries and industries. The congress was a pacifist meeting that discussed and promoted the ideals of peace and arbitration. |
20th Century
|
Year |
Event |
Description |
|
1902 |
Electric trams begin operating |
Antwerp introduces electric trams as a modern means of public transportation, replacing the old horse-drawn carriages. |
|
1903 |
World Gymnastics Championships held |
Antwerp hosts the 8th edition of the World Gymnastics Championships, the first time the event is held outside of Europe. |
|
1904 |
Museum Mayer van den Bergh built |
The museum displays the collection of art and antiquities of Fritz Mayer van den Bergh, a wealthy Antwerp collector who died in 1901. |
|
1905 |
Antwerpen-Centraal railway station and "America dock" open |
The railway station is a monumental building in eclectic style, designed by Louis Delacenserie. The dock is a large basin for transatlantic ships, connected to the Scheldt by a lock. |
|
1906 |
Fort Breendonk built |
The fort is part of the second ring of fortifications around Antwerp, designed to protect the city from a possible German invasion. |
|
1907 |
Eisenmann Synagogue built |
The synagogue is a striking example of Moorish Revival architecture, inspired by the Alhambra in Granada. It is named after the Eisenmann family, who donated the land for its construction. |
|
1910 |
Population: 361,723 |
Antwerp is the second most populous city in Belgium, after Brussels. |
|
1914 |
Siege of Antwerp; German occupation begins |
During World War I, Antwerp is besieged by the German army for a month, before surrendering on 10 October. The city remains under German occupation until 1918. |
|
1920 |
1920 Summer Olympics held |
Antwerp hosts the 7th edition of the modern Olympic Games, the first after World War I. The games are marked by the absence of Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey, as well as the introduction of the Olympic flag and oath. |
|
1923 |
Airport opens |
The Antwerp International Airport is inaugurated, becoming the first airport in Belgium to offer scheduled flights. |
|
1928 |
Antwerpsche Diamantkring established |
The Antwerpsche Diamantkring is the first diamond bourse in the world, founded by a group of diamond traders and brokers. It is located in the heart of the Antwerp diamond district. |
|
1930 |
Eeuwfeestkliniek (hospital) built |
The hospital is built to commemorate the 100th anniversary of Belgium's independence. It is designed by Jos Smolderen in Art Deco style. |
|
1931 |
Antwerp Book Fair begins |
The Antwerp Book Fair is the oldest and largest book fair in the Benelux region, attracting hundreds of publishers and thousands of visitors every year. |
|
1932 |
Boerentoren built |
The Boerentoren (Farmers' Tower) is a 26-story skyscraper, the first of its kind in Europe. It is the headquarters of the Kredietbank, a Belgian bank. |
|
1933 |
Museum of Flemish Literature founded |
The museum is dedicated to the history and development of Flemish literature, from the Middle Ages to the present day. It is housed in the former residence of the writer Hendrik Conscience. |
|
1940 |
German occupation begins |
During World War II, Antwerp is occupied by the German forces for a second time, after a brief and fierce battle. The city suffers from bombings, raids, and deportations. |
|
1944 |
Liberation by the British 11th Armoured Division; Battle of the Scheldt |
On 4 September, Antwerp is liberated by the British troops, who enter the city without much resistance. However, the port remains inaccessible until November, due to the German control of the Scheldt estuary. The Battle of the Scheldt is a crucial operation to secure the supply lines for the Allied forces. |
|
1946 |
Rubens House museum opens |
The museum is located in the former house and studio of Peter Paul Rubens, the famous Baroque painter. It displays his paintings, drawings, and personal belongings, as well as works by his contemporaries. |
|
1966 |
Sporthal Arena built; Wide White Space Gallery opens |
The Sporthal Arena is a multi-purpose indoor arena, used for sports, concerts, and other events. The Wide White Space Gallery is a pioneering venue for contemporary art, featuring works by Marcel Broodthaers, Joseph Beuys, Daniel Buren, and others. |
|
1967 |
Antwerp International School established |
The Antwerp International School is a private school that offers education in English for students from kindergarten to grade 12. It follows the International Baccalaureate curriculum. |
|
1968 |
De Tijd newspaper begins publication |
De Tijd (The Times) is a Flemish daily newspaper, focusing on business and financial news. It is the successor of the De Financieel-Economische Tijd, founded in 1961. |
|
1969 |
Jazz Middelheim festival begins; Kennedytunnel opens; Royal Ballet of Flanders established |
The Jazz Middelheim is an annual jazz festival, held in the Middelheim Park. It features local and international artists, and attracts thousands of fans. The Kennedytunnel is a road and rail tunnel under the Scheldt, connecting the left and right banks of the river. It is named after the US president John F. Kennedy. The Royal Ballet of Flanders is the official ballet company of Flanders, based in Antwerp. It performs classical and contemporary ballets, and tours nationally and internationally. |
|
1970 |
Chicagoblok built |
The Chicagoblok is a social housing complex, consisting of three high-rise buildings and a lower block. It is designed by Renaat Braem, a prominent Belgian architect and urban planner. |
|
1975 |
Antwerp Pre-metro begins operating |
The Antwerp Pre-metro is a network of underground tram lines, serving the city center and the suburbs. It is called pre-metro because it is intended to be converted into a full metro system in the future. |
|
1977 |
't Fornuis restaurant in business |
't Fornuis (The Stove) is a Michelin-starred restaurant, specializing in traditional Flemish cuisine. It is run by chef Johan Segers, who is known for his use of local and seasonal ingredients. |